What Does Rpa Stand for in Banking
Fintech |Written by Viktor Antonenko
Reading time: 6 minutes
Advanced technologies paired with new approaches and methodologies to handle immense amounts of data have been sweeping the world and turning the economy from analog to digital. As a data-driven industry, the financial services sector must be at the forefront of this revolution. However, the current status of banks' digital transformation is far from being exemplary.
According to the , a staggering 81% of banking executives are overwhelmed by the speed of technological change that calls for constant refinement and restructuring of business processes. That fear is fueling the doubts to start integrating automation, which has become a mainstay of the digital age.
Let's find out to what challenges CEOs have to rise to start the successful digital transformation with simple yet efficient robotic process automation (RPA).
ABCD of Technologies
Being driven by digital technologies, the disruption of the financial services industry has resulted in a paradigm shift of how consumers prefer to interact with banks. To meet the new expectations and thrive in a constantly changing environment, banks have been adopting 4 major digital technologies. You may know them under the ABCD acronym, which stands for Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, Cloud, and Data analytics. Automation is the first stage of AI, which helps companies recalibrate business processes to prepare traditional business models for shifting from a closed system to an open architecture. To learn more about the current technological landscape of the banking industry, read our .
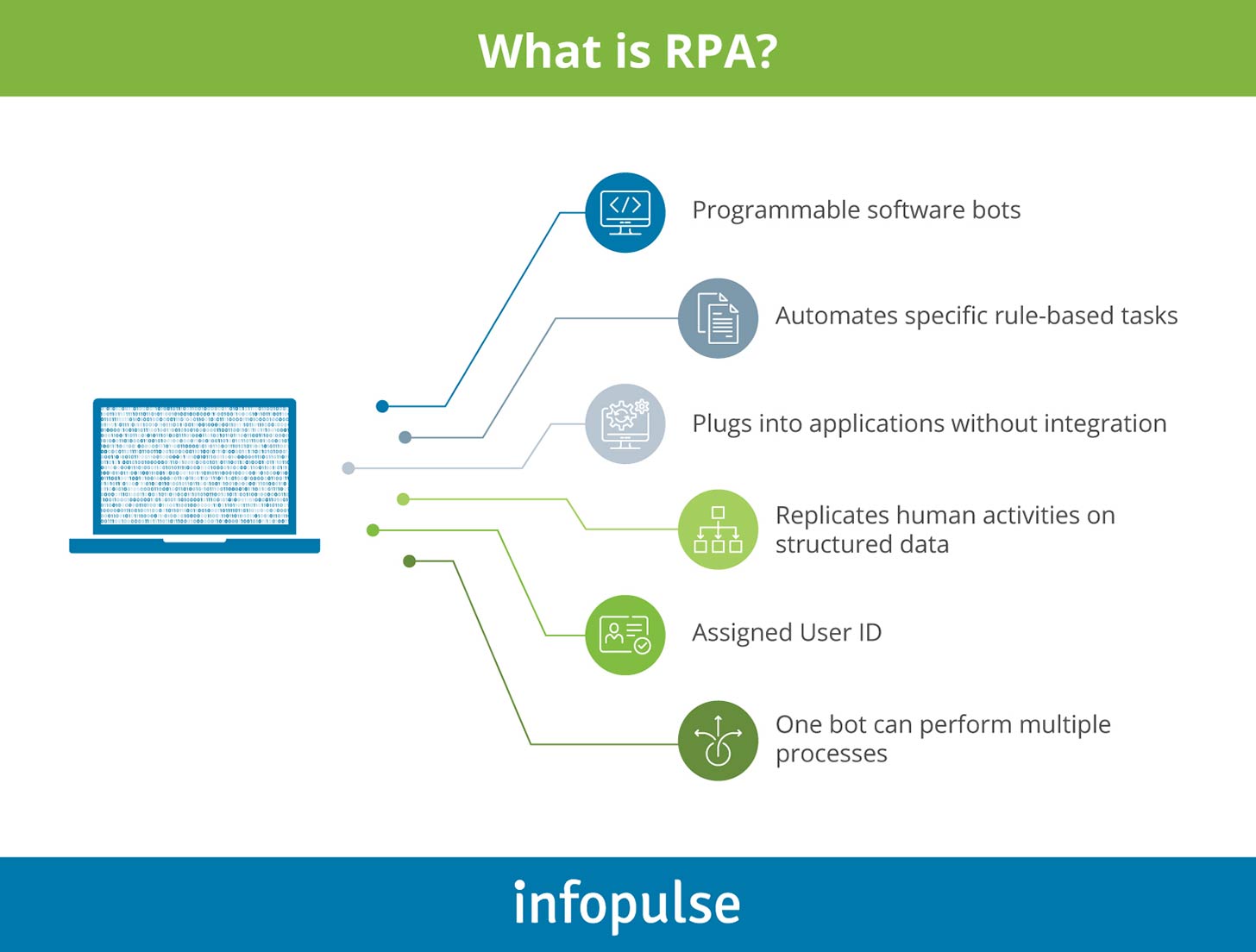
RPA (robotic process automation) was developed to address the challenge of continuously growing routine processes by automating repetitive and rule-based tasks with simple software bots. By following pre-programmed rules, software robots automate high-volume business processes that result in optimized costs, operational accuracy, and better talent management. For example, one of the most common RPA use cases in banking is customer inquiry processing. RPA helps to deal with modern consumers' high requirements for the brand they interact with, as they expect quick and personalized service on transparent terms.
Before the advent of RPA, automation options were cumbersome to integrate and limited in scope. For example, simple macros were popular with Microsoft Office applications like Excel spreadsheets. Another example would be traditional IT process automation solutions that exploit APIs to enable the connection between enterprise applications. The major advantage of RPA over traditional automation solutions is that it functions on top of applications and mimics human actions at the user interface level. Thus, in order to function properly, RPA software doesn't require changes in the existing applications, nor does it require their replacement.
Amplifying Productivity and Employee Satisfaction with Ease
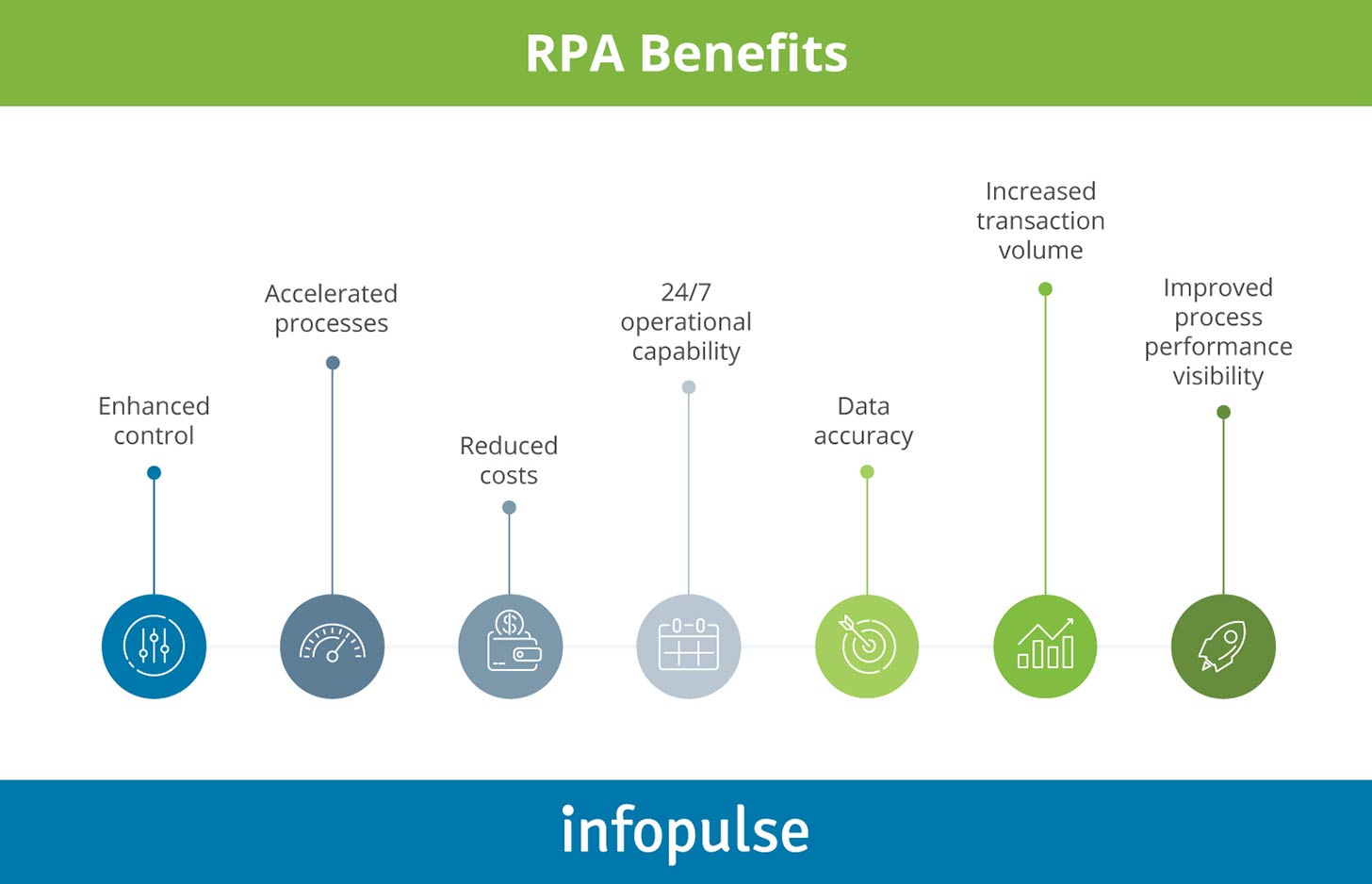
In the financial world, RPA capabilities are truly transformative, e.g., the ability to streamline the front client-facing office, improve risk management, strengthen the compliance of the middle office, and accelerate behind-the-scenes settlements and clearance operations of back offices.
Strangely enough, back-office banking practices still contain never-ending burdens of paperwork that require lots of time and practically no skills to be completed. Apart from transforming financial forecasting, personalized financial services, and data management, RPA solutions can seamlessly automate all of the following processes:
- Provide efficient customer service – from application status to balance information
- Process bill payments – by extracting and validating information for payment processing
- Grant mortgage – by processing credit checks, repayment history, and employment verification
- Update general ledger with financial data
- Conduct data migration
- Maintain compliance
- Process fraud detection and much more.
Despite the obvious and tangible benefits of robotic process automation, banking industry leaders are slowly approaching the RPA technology adoption. As the IT landscape continues to grow in complexity, it becomes more difficult to integrate and automate processes across multiple systems. This stumbling point entails a handful of challenges that leaves leading players skeptical about the total digitization of the banking system.
Common Obstacles on the Way to RPA Adoption
It has only been 5 years since robotic process automation became an integral part of digital transformation. Despite some challenges, RPA adoption and scaling have matured enough to become a must for savvy companies. Let's take a closer look at those challenges, their underlying causes, and some practical ways of dealing with them.
1. Resistance to Change
According to , 45% of respondents from leading financial organizations listed resistance to adoption as the top challenge stopping them from embracing RPA. These results demonstrate the fact that despite the technology maturity, its adoption has turned into a business challenge as opposed to a technology one.
The shift in mindset and change management are the primary goals that need to be met before embracing any technology. RPA adoption is just a starting stage of the enterprise-wide automation strategy. Sadly, the automation strategy cannot be properly and effectively executed without implementing organizational change management as part of the holistic approach towards technology acceptance.
A great example of strong governance and advanced planning would be the . In 18 months, one of the largest American banks was able to successfully deploy 22 robots across its front, middle, and back offices that already saved the organization $100,000 per code request in operational costs.
2. Process Standardization and Organizational Difficulties
, Deloitte included process standardization and organizational misalignment among the top challenges in implementing RPA in banking. The difficulty is rooted in the traditional separation of IT and business departments that handle different operations. To integrate RPA solutions in an organization, a new distribution of roles and responsibilities is required to create an alignment between the teams involved. This hurdle, in turn, implies the challenge of process standardization related to unstructured data and non-standardized processes that require human input. Oftentimes, things go wrong at the initial stage when it is needed to decide exactly which business processes will be automated. The problem here is that the same processes can be understood and executed differently.
, provided by Deloitte in another RPA report, demonstrates this problem in action. Even after a year of struggle, they couldn't deploy RPA due to the lack of top management support and no IT capabilities included in the RPA team. The company solved the problem by appointing a dedicated manager to organize and perform the proper allocation of roles and resources. This case only proves the importance of communication and cooperation in the decision-making process, which are so often overlooked.
3. Compatibility with Legacy Infrastructure
The thirds most common obstacle to RPA adoption is the slow pace of technological development in the banking industry. Despite being one of the most data-driven domains, the financial sector is lagging behind in digital transformation. Most banking platforms, on which core systems of the finance institutions run today, were developed in the 1970s. The scope of this problem is huge, with Reuters reporting that almost , a programming language from the 1950s. Such outdated tech stack is obviously not compatible with digital age technologies. Legacy system replacement projects are massive and expensive, and, on top of that, they pose risks that banks are not ready to mitigate.
However, postponing the unavoidable restructuring process makes it only more expensive and prone to risks. This is why pursuing a digital transformation strategy should be a wholesome and overarching process.
4. Lack of Legal Regulations Governing Automation
Along with the undoubtful benefits of introducing innovation on a wide scale, adopting RPA in the banking industry entails some legal requirements and constraints for process automation. Even though RPA was developed in the 2000s, it actively started entering the market only after 2015. That is why the technology is relatively young in terms of legal regulations it requires to be implemented – the ones issued by the central banks, the government, and other parties. Those legal regulations are still lacking in many countries.
Thus, states that data subjects have the right not to be subjected to a decision based on automated processing. With the criteria being unclear and ambiguous, it is hard to tell whether a bank assessing a person's credit risk with algorithmic card scoring fits the standards laid out in Article 22. As the technology matures and becomes a must for more financial institutions, the burden of regulatory complexity is slowly but steadily being eased by digital transformation agents and tools.
Rising to the Challenges Together
Even though adopting RPA may seem daunting at first, it brings invaluable benefits and competitive advantages for the banks operating in the digital economy. On closer inspection, we have seen that causes underlying major obstacles to embrace the power of RPA are grounded in our natural resistance to change and poor communication. Still, the potential to accelerate and streamline business processes and scale up your organization definitely outweighs a few pain points associated with RPA implementation.
If you want to start a holistic digital transformation of your company, Infopulse can help you with developing intelligent RPA solutions ranging from basic automation to sophisticated solutions. Please, contact us directly and get a free consultation on the RPA options best suited for your business.

Viktor Antonenko
RPA Team Leader
Viktor Antonenko is an expert RPA engineer with 10+ years of background in ensuring operational excellence for industry-leading financial institutions. He holds numerous RPA-related certifications and has extensive experience in Robotic Process Automation (UiPath, BluePrism, PowerAutomate), Elasticsearch/Kibana technologies and process analisys, re-engineering and optimization. His achievements were recognized with a High Performance Award.
Originally published November 23, 2020 Updated January 15, 2021
What Does Rpa Stand for in Banking
Source: https://www.infopulse.com/blog/challenges-robotic-process-automation-banking/